Apple researchers have unveiled a groundbreaking framework designed to make non-humanoid robots move more naturally and expressively during human interactions. This innovation could significantly enhance robotic assistants' appeal in homes and workplaces. Published this month on arXiv—a free online archive of scholarly articles in the fields of science, technology, and engineering—the study introduces the Expressive and Functional Movement Design (ELEGNT) framework. This system enables robots to convey emotions, intentions, and attitudes through their movements, rather than simply executing functional tasks.
“For robots to interact more naturally with humans, movement design should integrate expressive qualities—such as intention, attention, and emotions—alongside traditional functional considerations like task fulfilment, spatial constraints, and time efficiency,” Apple’s robotics research team explained in their paper.
Testing Robot Emotions: The Desk Lamp Experiment
To test the effectiveness of expressive movements, the researchers used a lamp-like robot resembling Pixar’s Luxo Jr. The robot, equipped with a 6-axis robotic arm and a head containing a light and projector, was programmed with two movement styles: one focused purely on task completion and the other designed to convey expressiveness. User testing with 21 participants revealed that expressive movements significantly enhanced engagement and perception of the robot. This effect was particularly noticeable in social interactions, such as playing music or casual conversations. However, when it came to functional tasks like adjusting lighting, expressive movements had less impact.
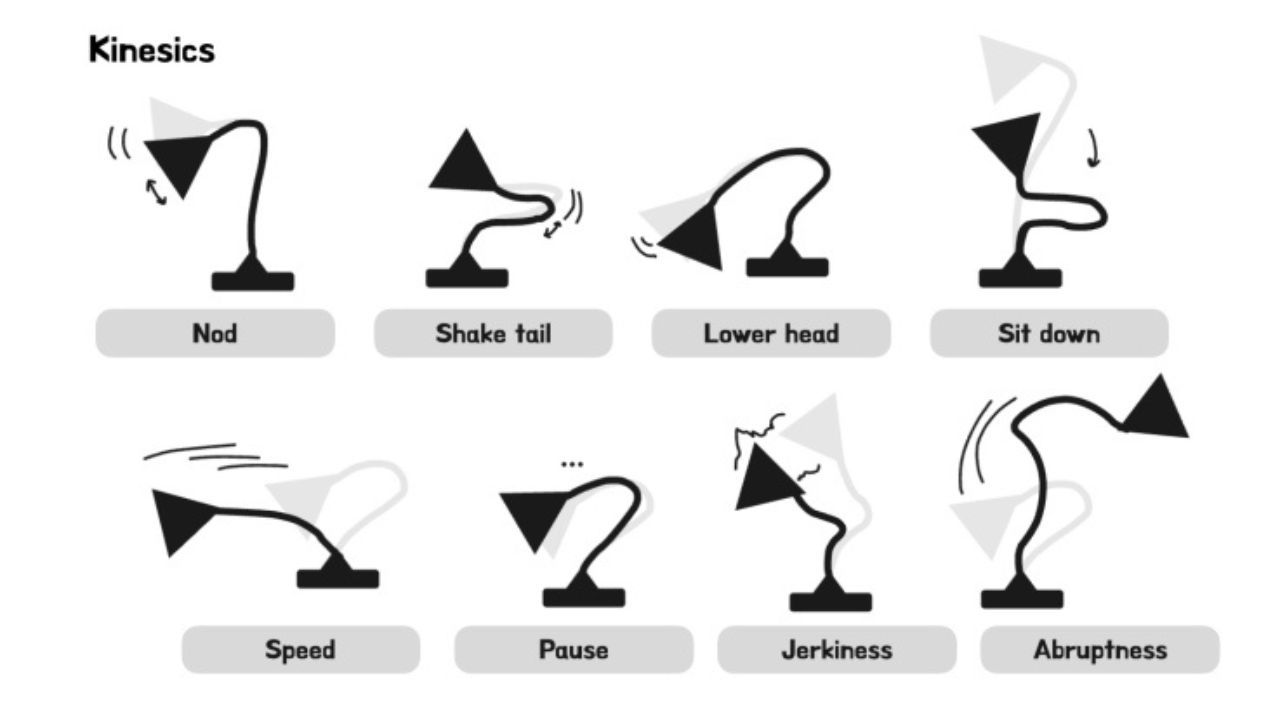
One participant noted, “Without the playfulness, I might find this type of interaction with a robot annoying rather than welcome and engaging.” This highlights how expressive movements can make even intrusive robot actions feel more acceptable and engaging.
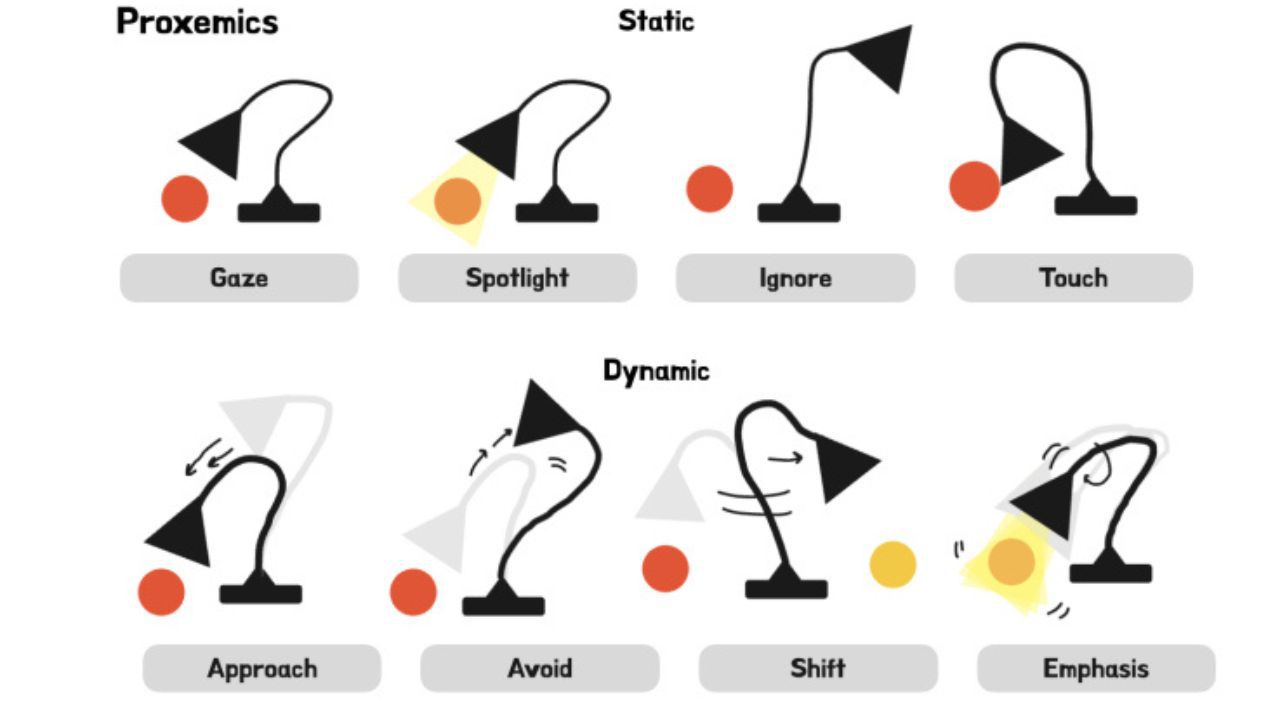
Balance Between Efficiency & Engagement
As major tech companies continue to explore home robotics, Apple’s research suggests that natural, expressive movements could make future robots more appealing as companions. However, the study also emphasises the importance of balance. “There needs to be a balance between engagement through motion and the speed of task completion; otherwise, the human might grow impatient,” one participant observed. This finding underscores the need for a careful balance between expressiveness and efficiency in robot design.
Preferences in Robot Movement
Interestingly, the study found a notable age gap in user preferences regarding expressive robot movements. Older participants were generally less receptive to these movements, suggesting that robot behaviours may need to be customised based on the user’s age and preferences.
Apple’s Vision for Future Home Robots
While Apple rarely discusses its robotics research publicly, this study offers a glimpse into how the company might approach future home robots. It represents a fundamental shift in robotics design—moving beyond what robots can do and focusing on how they make people feel.




